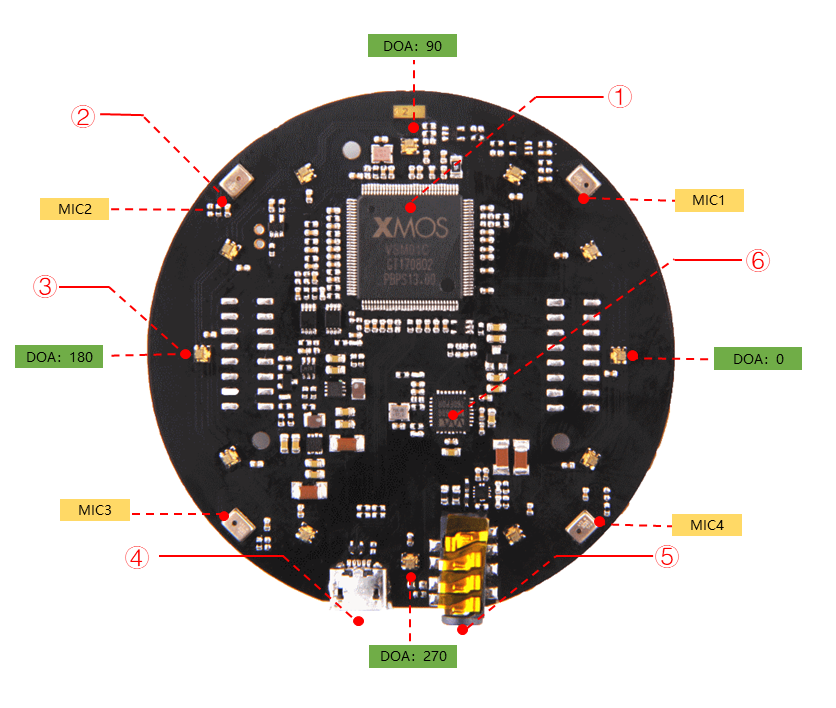
Microphone array and audio recording#
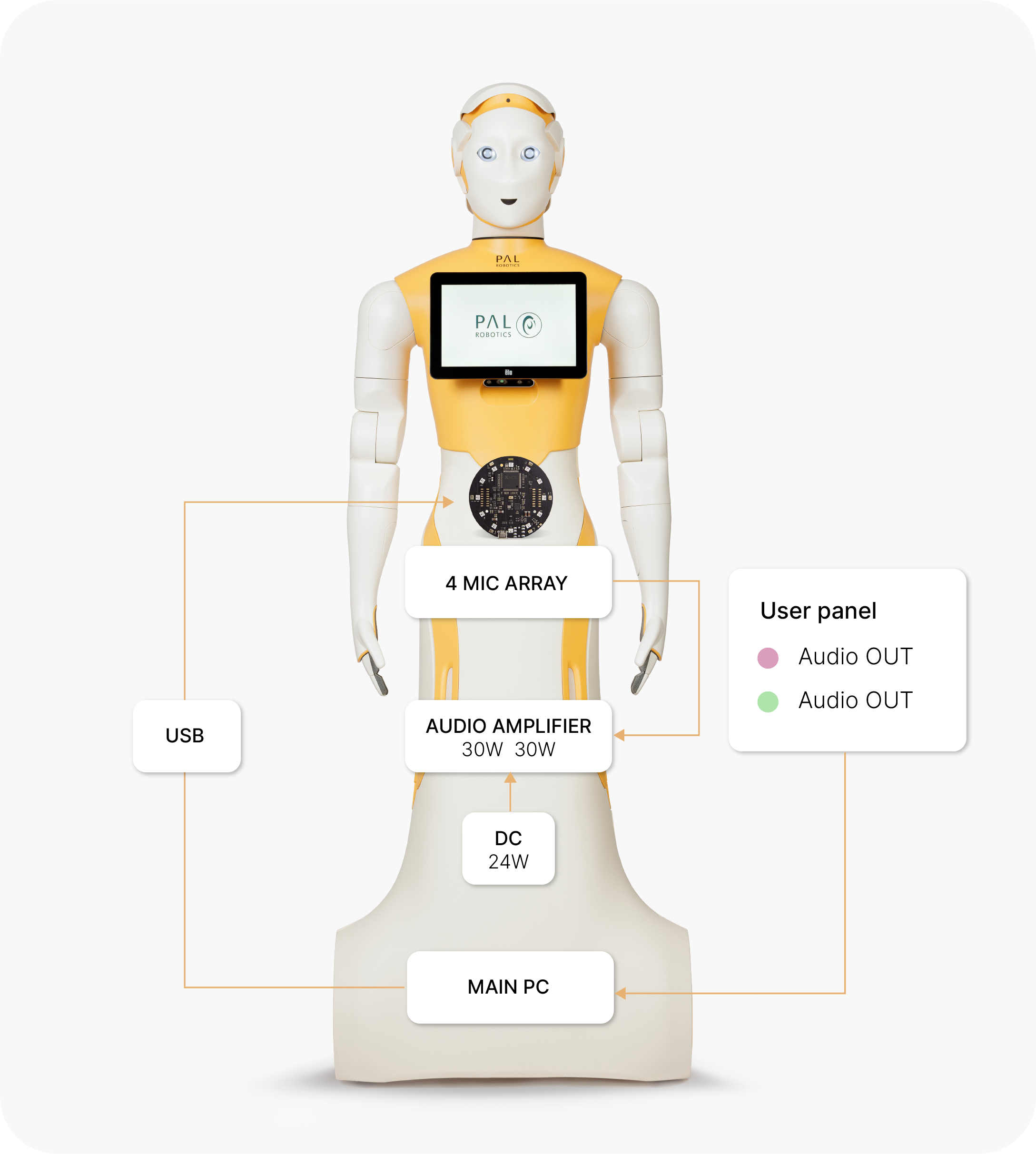
ARI has a ReSpeaker Mic Array V2.0 consisting of 4 microphones, positioned in the torso, just below the touch-screen (ARI).
Caution
TIAGo (v1) features a simple microphone. Some of the features available on robots equipped witht he reSpeaker microphone array (like sound source localisation or noise cancellation) are therefore not available on this robot.
The microphone is connected via USB to the main PC. The PC then outputs audio through the robot’s two speakers, located at each lateral side of the torso, that include a 30W amplifier.
Main hardware features:
Support USB Audio Class 1.0 (UAC 1.0)
Four microphones array
Sensitivity: -26 dBFS (omnidirectional)
Signal-to-Noise Ratio: 63dB
12 programmable RGB LED indicators
Note
By default, the microphone LEDs are configured to turn blue when the microphone hears something. In addition, a light blue LED indicates the current sound source direction.
The parameter enable_leds can be set to False in the respeaker_ros
launch file to disable this behaviour.
The ReSpeaker microphone also implements several audio processing directly on the hardware:
far-field Voice Activity Detection (up to 5m away);
Direction of Arrival (DoA) estimation;
Beamforming (BF) to focus on sound coming from a specific source;
noise suppression;
de-reverberation;
acoustic echo cancellation, enabling the robot to ignore its own voice.
ROS API#
PAL’s robots relies on an heavily modified version of the open-source respeaker_ros driver.
It exposes the following topics:
/audio/raw: Merged audio channel of the 4 microphones (alias for /audio/channel0).
/audio/channel0: Merged audio channel of the 4 microphones
/audio/channel1: Audio stream from the first microphone.
/audio/channel2: Audio stream from the second microphone.
/audio/channel3: Audio stream from the third microphone.
/audio/channel4: Audio stream from the fourth microphone.
/audio/channel5: Monitor audio stream from the audio input (used for self-echo cancellation).
/audio/voice_detected: Publishes a boolean indicating if a voice is currently detected (ie, whether someone is currently speaking)
/audio/speech: raw audio data of detected speech (published once the person has finished speaking).
/audio/sound_direction: The estimated Direction of Arrival of the detected sound.
/audio/sound_localization: The estimated sound source location.
Audio can then be recorded as a rosbag, for example:
ssh pal@<robot>-0c
rosbag record -O audio_sample.bag /audio/channel0
Regardless on how the audio is captured, it can later be processed.
Recording audio directly from ALSA#
You can also access the ReSpeaker as a regular Linux ALSA recording device:
log onto the robot and it should appear when running the command arecord -l
(and arecord -L to get the list of ALSA device names).
To record, you first need to stop the ROS driver and find the correct device name
in the arecord -L list. In the example below we are recording it
at 16 KHz sampling rate, recording all 6 channels of the respeaker, for a
duration of 10 seconds.
> pal-stop respeaker_ros
> arecord -D "hw:CARD=ArrayUAC10,DEV=0" -fS16_LE -c6 -d 10 -r16000 > audio.wav
Play back the recorded sound:
> aplay audio.wav
You can then re-enable the ROS interface:
> pal-restart respeaker_ros