Speech synthesis (TTS)#
Overview of the technology#
Your robot incorporates the Acapela Text-to-Speech from Acapela Group.
The technology used in this engine is the one that leads the market of synthetic voices. It is based on unit selection and allows to produce highly natural speeches in formal styles. The system is able to generate speech output, based on a input text utterance [1]. It does the phonetic transcription of the text, predicts the appropriate prosody for the utterance and finally generates the signal waveform.
Every time a text utterance is sent to the text-to-speech (TTS) engine it generates the corresponding waveform and plays it using the robot speakers. There are several ways to send text to the TTS engine: using the ROS API, by executing ROS commands in the command line or by implementing a client in C++. Each of them is described below.
Text-to-Speech node#
Launching the node#
To be able to generate speeches, the soundServer should be running
correctly.
System diagnostics described in section WebCommander allow to check the status of the TTS service runing in the robot. These services are started by default on start-up, so normally there is no need to start them manually. To start/stop them, the following commands can be executed in a terminal opened in the multimedia computer of the robot:
pal-start sound_server
pal-stop sound_server
Action interface#
See /tts
Examples of usage#
WebCommander#
Sentences can be synthesized using the WebCommander, a text field is provided so that text can be
written and then synthesized by pressing the Say button.
Additionally buttons can be programmed to say predefined setnences, see the Commands Plugin Configuration for details.
Several buttons corresponding to different predefined sentences are provided in the lower part of the Demos tab, as shown in figure below.
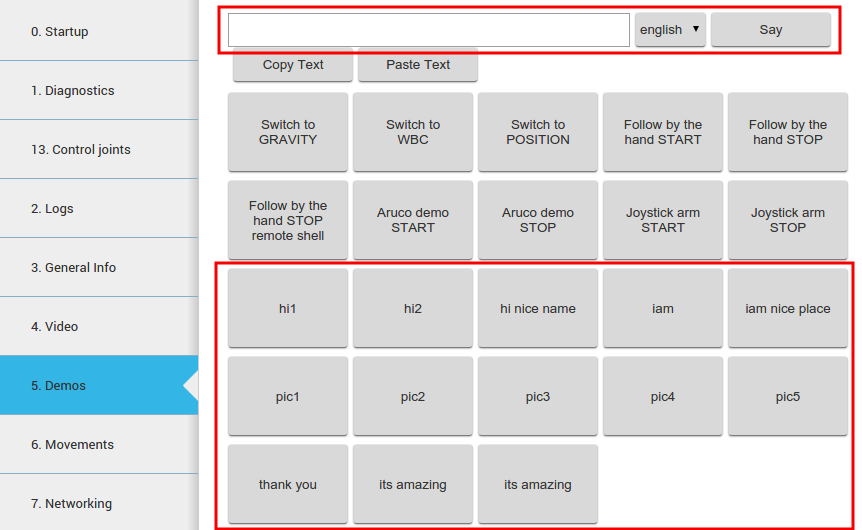
Figure: Voice synthesis in a commands tab of the WebCommander#
Command line#
Goals to the action server can be sent through command line by typing:
rostopic pub /tts/goal pal_interaction_msgs/TtsActionGoal
Then, by pressing Tab the required message type will be auto-completed. The fields under
rawtext can be edited to synthesize the desired sentence, as in the following example:
rostopic pub /tts/goal pal_interaction_msgs/TtsActionGoal "header:
seq: 0
stamp:
secs: 0
nsecs: 0
frame_id: ''
goal_id:
stamp:
secs: 0
nsecs: 0
id: ''
goal:
text:
rawtext:
text: 'Hello world'
lang_id: 'en_GB'
speakerName: ''
wait_before_speaking: 0.0"
Action client#
A GUI included in the actionlib package of ROS Melodic or actionlib_tools in ROS Noetic
can be used to send goals to the voice synthesis server.
In order to be able to execute the action successfully, the ROS_IP environment variable should
be exported with the IP direction of your development computer:
export ROS_IP= # your IP address
The GUI shown in Figure: Voice synthesis using the GUI from actionlib below can be run as follows:
export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://tiago-0c:11311
# For ROS Noetic
rosrun actionlib_tools axclient.py /tts
Editing the fields inside rawtext parameter and pressing the SEND GOAL button will
trigger the action.
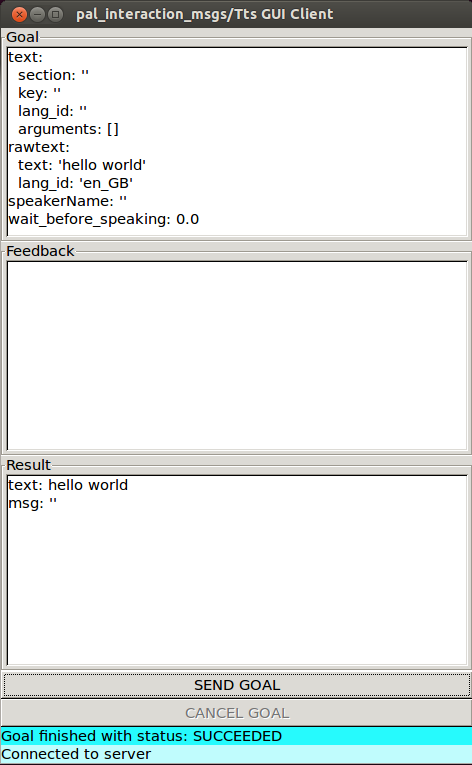
Figure: Voice synthesis using the GUI from actionlib#