Tutorial: Build and run a new ROS package#
🏁 Goal of this tutorial
By the end of this tutorial, you will know how to develop a new ROS package (C++ or Python) inside a Docker image.
Pre-requisites#
You need to be already familiar with ROS: if not, check the ROS tutorials.
In particular, you might want to check the catkin tutorials if you are new to catkin.
Steps#
This exercise can be done both in your development computer or inside the ARI docker.
From your main computer create a new catkin workspace:
1mkdir -p ~/example_ws/src
If you want to use the docker, run the ARI docker, mounting the newly created workspace. Make sure to map the workspace properly. Then load the ROS environment.
Note
For your convenience, we have published some scripts that simplify the launch of a docker with GPU acceleration. Follow the instructions at pal_docker_utils to properly set up your environment with nvidia-docker. If you do not follow the steps properly, you will not be able to run gazebo, rviz or other graphical applications from within the docker container.
Once logged and after configuring pal_docker_utils, you will need to execute
the pal_docker.sh
script with the name of the image and the application you want to start.
1./pal_docker.sh -it -v ~/docker_mounts/gallium:/home/user/ -v /home/user/example_ws:/home/user/example_ws/ PATH_TO_YOUR_DOCKER_IMAGE bash
2
3source /opt/pal/gallium/setup.bash
If you are working on your development computer, only source the ROS environment, in this case, ROS Noetic:
1source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash
Create a catkin package
1cd /home/user/example_ws/src/
2catkin_create_pkg hello_world roscpp rospy std_msgs
3cd hello_world
Configure the package depending on your language
Edit the CMakeLists.txt file with the contents in the figure below.
1cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.3)
2project(hello_world)
3
4find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS roscpp)
5
6catkin_package()
7
8include_directories(
9 SYSTEM ${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
10)
11
12## Declare a C++ executable
13add_executable(hello_world_node src/hello_world_node.cpp)
14target_link_libraries(hello_world_node ${catkin_LIBRARIES})
15
16## Mark executables and/or libraries for installation
17install(TARGETS hello_world_node RUNTIME DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_BIN_DESTINATION})
Edit the src/hello_world_node.cpp file with the contents in the figure below
1// ROS headers
2#include <ros/ros.h>
3
4// C++ std headers
5#include <iostream>
6
7int main(int argc, char** argv)
8{
9 ros::init(argc,argv,"hello_world");
10
11 ros::NodeHandle nh("~");
12
13 std::cout << "Hello world" << std::endl;
14
15 return 0;
16}
Create script folder and script
mkdir scripts
touch scripts/hello_world.py
Make the script executable
chmod +x scripts/hello_world.py
Edit the CMakeLists.txt file with the contents in the figure below.
1cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.3)
2project(hello_world)
3find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS
4 rospy
5)
6
7catkin_package()
8
9# Install Python scripts
10install (PROGRAMS scripts/hello_world.py DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_BIN_DESTINATION})
Edit the scripts/hello_world.py file with the contents in the figure below
1#!/usr/bin/env python
2#license removed for brevity
3import rospy
4from std_msgs.msg import String
5
6def talker():
7 pub = rospy.Publisher('hello', String, queue_size=10)
8 rospy.init_node('hello_world', anonymous=True)
9 rate = rospy.Rate(10) # 10hz
10 while not rospy.is_shutdown():
11 hello_str = "hello"
12 rospy.loginfo(hello_str)
13 pub.publish(hello_str)
14 rate.sleep()
15
16if __name__ == '__main__':
17 try:
18 talker()
19 except rospy.ROSInterruptException:
20 pass
Build the workspace in the same way, regardless if it is a Python or C++ script.
1cd ~/example_ws
2catkin build
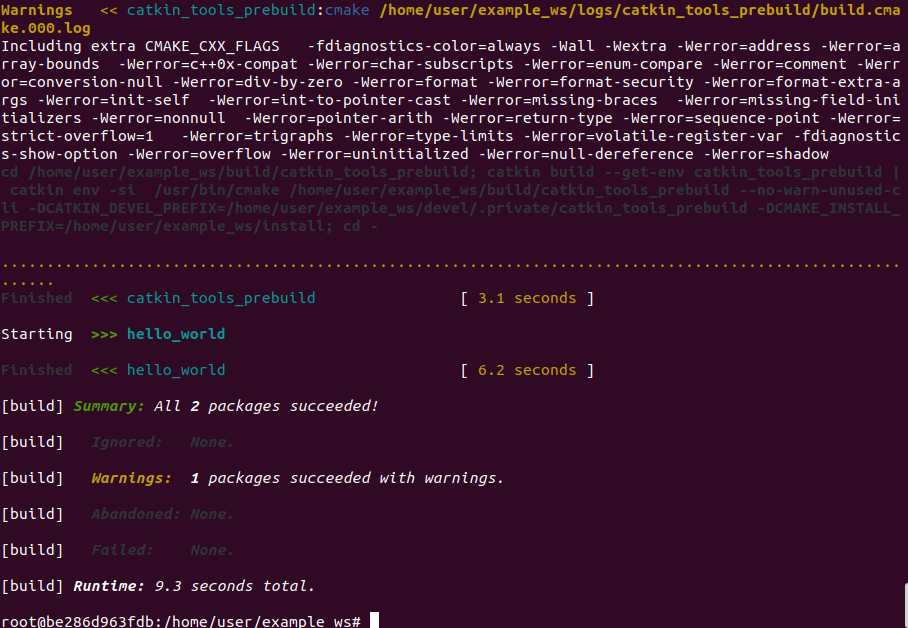
The expected output is shown in the figure below.
In order to run the node export the robot’s ROS_MASTER_URI and source the workspace:
1export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://ari-0c:11311
2
3source devel/setup.bash
4
5rosrun hello_world hello_world_node
For the Python node:
1rosrun hello_world hello_world.py
Check the message is correctly published by opening a new terminal. If it is the development computer:
1export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://ari-0c:11311
2rostopic echo /hello
Note, in this last step, if you are using a docker, open a new docker instance first:
1docker exec -it IMAGE_ID bash
2
3source /opt/pal/gallium/setup.bash
4
5export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://ari-0c:11311
6
7rostopic echo /hello
Where the IMAGE_ID is obtained by listing available dockers.

If no message is obtained, make sure the ROS_IP is correctly set. Check inside
the robot its IP address with ifconfig.
1export ROS_IP=192.168.1.109